Identification of Material Topics
Analysis of Material Topics
FEDS references the AA1000 Accountability Principles, GRI Sustainability Standards, domestic and international sustainability development trends, as well as topics of concern to domestic industry peers and stakeholders as the basis for materiality assessment and report disclosure. FEDS conducts an annual review of material topics, evaluating their impacts on economic, environmental, and social (including human rights), and uses the identification results as a reference for sustainability management actions and to enhance the quality of sustainability decision-making.
Identify Topics
I. Understanding Organizational Context
According to the AA1000 SES stakeholder engagement principles—dependence, responsibility, influence, diversity of perspectives, and level of concern—FEDS has identified six major categories of stakeholders: consumers, employees, business partners (counter vendors and suppliers), shareholders/financial institutions, government, and society (media and community).
II. Identification of actual and potential impacts
Referring to domestic and international sustainability regulations and standards, industry environmental changes, company development goals, and stakeholder concerns, 38 sustainability issues were identified. After discussion by the Corporate Sustainability Committee Executive Office and consideration of related sustainability risks, these were refined to 13 sustainability issues, which were then subjected to a questionnaire survey.

III. Assessment of impact severity
Through a questionnaire survey, FEDS assessed the impact of sustainability issues on the external economy, environment, and people (including human rights) as perceived by six major stakeholder groups. Although 765 questionnaires were originally planned for distribution, a total of 842 were actually collected, comprising consumers (337), employees (295), business partners (127), shareholders/financial institutions (23), government (17), and society (43). Additionally, 19 internal management questionnaires were conducted to evaluate the extent of sustainability issues’ impact on the company’s operations.
Based on a comprehensive analysis of internal and external survey results, as well as a review of management policies, implementation measures, and sustainability outcomes, 13 material topics were ultimately identified, including 7 key topics, 3 important topics, and 3 basic topics.
Compared to the previous year:
“Social Welfare” was added; “Energy Management” and “Water and Waste Management” were consolidated into “Energy and Resource Management”; “Integrity Management” and “Regulatory Compliance” were consolidated into “Integrity Management and Regulatory Compliance.”
Regarding material changes:
“Integrity Management and Regulatory Compliance,” ” Occupational Safety and Health ,” and “Business Performance and Innovation Strategy” have been elevated from important topics to key topics. “Talent Development and Retention” has been downgraded from an important topic to a basic topic. The materiality of the remaining nine topics remains unchanged.
IV. Ranking impact severity and disclosure
Sent the “Impact Assessment Questionnaire” to 12 department heads to rate the positive and negative impact levels of major topics on external economy, environment, and people (including human rights). The impact assessment considered both the likelihood of occurrence and the scale and scope of impact, and was submitted for the approval of the President.
Conducted final confirmation and review of material topics, continuously monitoring the positive and negative impacts caused by these material topics, and considering stakeholders’ expectations. This will serve as a reference for the appropriateness of material topics for the following year, while ensuring that sustainability information and performance are fully disclosed.
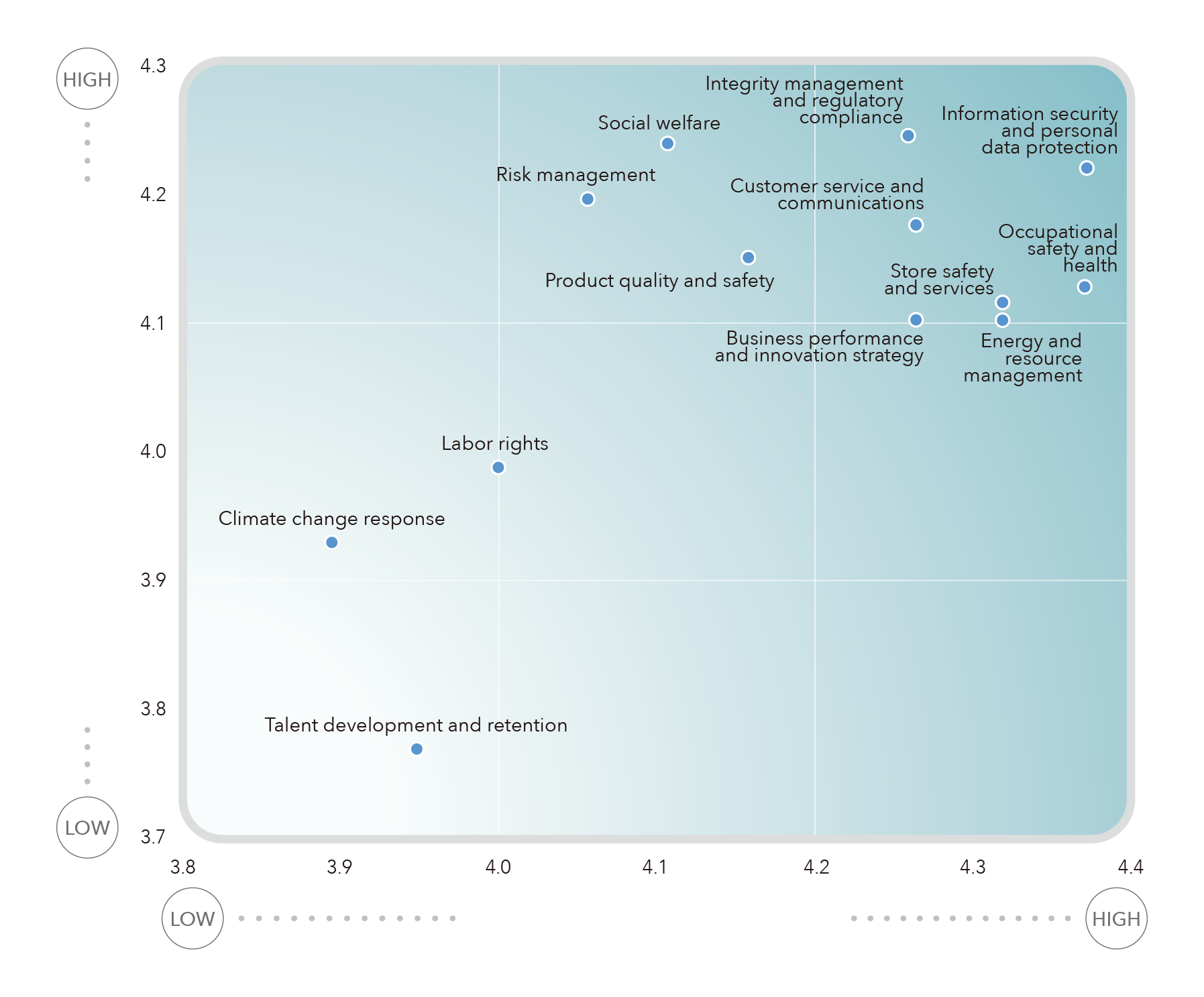
Material Topic Matrix
Impact Assessment
FEDS adopts the Double Materiality principle, identifying 13 material topics. Through comprehensive analysis, the impact levels of these topics were ranked, including the top five impacts across various dimensions. Among them, “Climate Change Response” was identified as having the highest positive impact, prompting the enhancement of management policies to expand positive effects. Conversely, “Energy and Resource Management” was found to have greater negative impacts than positive ones, leading to strengthened management actions to reduce the environmental negative impacts of operational activities.
In February 2025, a gas explosion occurred in the department store industry in Taichung, marking a major public safety incident. Following the incident, local governments across various cities launched public safety inspection projects to prevent similar accidents. All FEDS branches throughout Taiwan passed the safety inspections with no safety deficiencies found. At the same time, FEDS initiated internal patrols to ensure safety and health of the workplace and the store. This allowed customers to shop with confidence and staff to work securely.
Impact Assessment Results of Material Topics
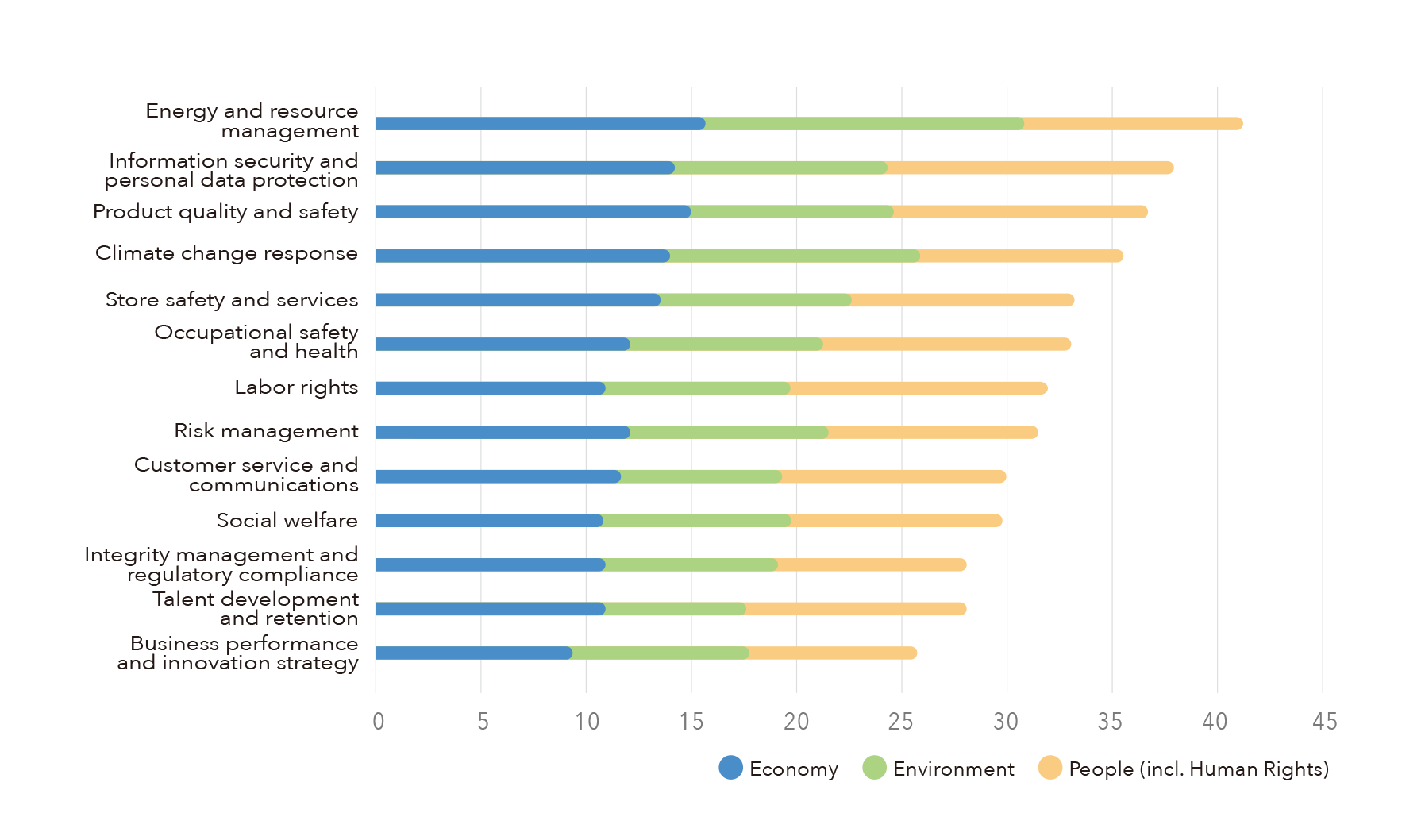
Top 5 in Terms of Economic,
Environmental and Human Rights Impacts
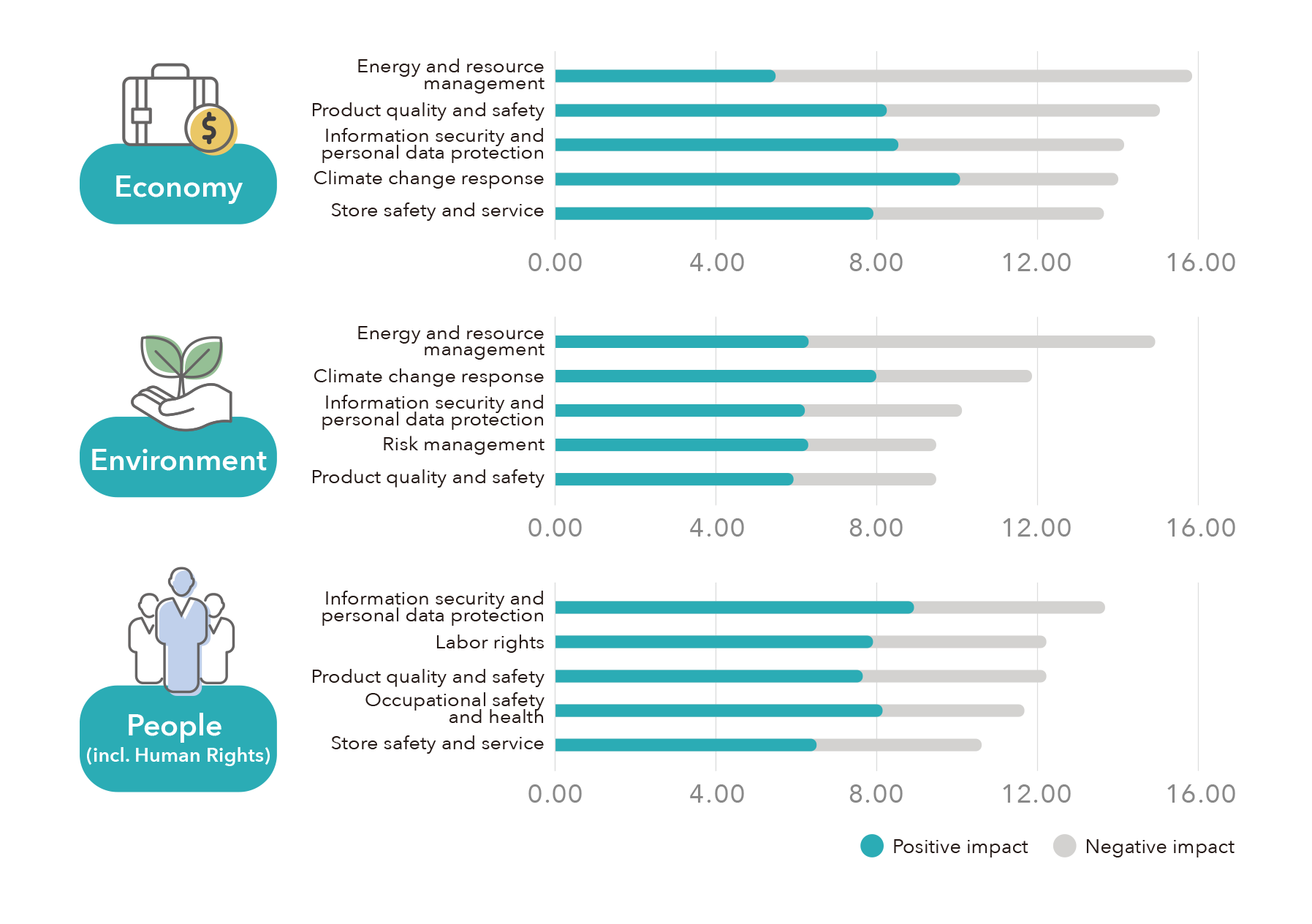
經濟、環境、人權衝擊排序前5名
經濟
環境
人權
Impact Description and Management
| Material topics | Policy and Commitments | Impact Description |
| Energy and resource management | Promote actions in energy conservation, carbon reduction, green energy, and waste reduction to improve energy efficiency, implement resource sustainability, and reduce environmental impact. | Energy consumption not only affects operating costs but is also a major source of carbon emissions. Improving energy efficiency and the proportion of renewable energy will have positive impacts on both the economy and the environment. |
| Information security and personal data protection | Establish cybersecurity procedures and standards to carefully protect corporate information security and ensure the safety of critical information. | Establish a cybersecurity alert and reporting mechanism to reduce the risks of cybersecurity breaches and personal data leaks, positively impacting the economy and human rights. |
| Product quality and safety | To ensure consumers receive high-quality products, FEDS complies with laws and regulations regarding the inspection, labeling, and management of the goods sold, allowing customers to shop with confidence. | Providing safe and high-quality products ensures the health and safety of customers, earns their trust, and avoids related legal risks. |
| Climate change response | Establish a climate risk assessment and management mechanism to enhance climate resilience and advance toward low-carbon sustainability. | Properly managing strategies related to climate change issues can reduce impacts on revenue, costs, assets, and operations, yielding positive economic and environmental benefits. |
| Store safety and services | Create a shopping environment that is safe, convenient, healthy, and environmentally friendly, providing consumers with a comfortable and enjoyable shopping experience. | Make detailed arrangements in facilities, traffic flow planning, and service design to provide a safe shopping environment and services while reducing negative environmental impact. |
| Occupational safety and health | Establish the Occupational Safety and Health Committee to promote health programs and provide employees with a friendly and safe working environment. | Promote various workplace safety and health programs to create a safe working environment and enhance positive impacts on the economy and human rights. |
| Labor rights | FEDS values labor rights, establishes and implements related policies, provides a dignified and safe working environment, and protects labor rights. | Failure to uphold labor rights will affect corporate reputation and employee loyalty. Comprehensive management measures can protect the rights and interests of employees and other stakeholders. |
| Risk management | Established the Risk Management Policy to effectively identify, measure, monitor, and control various risks, ensuring that company operations remain unaffected by disruptions. | Establish a sound risk management mechanism to mitigate the economic, environmental, and social impacts that the company’s operations and future development may face. |
| Customer service and communications | Establish a comprehensive service system, attentively listen to customer needs, and treat every customer with kindness, enthusiasm, and professionalism. | FEDS has established effective service procedures and communication channels to maintain long-term trust with customers, thereby indirectly promoting economic growth. |
| Social welfare | Adhering to the spirit of “taking from society and giving back to society,” FEDS has transformed each of its business locations into a “public welfare platform” to promote various charitable activities. | Leveraging its distribution network, FEDS utilizes resources to invest in social welfare, focusing on rural areas, women and children, and environmental issues. The company collaborates with charitable organizations and business partners to create shared social benefits. |
| Integrity management and regulatory compliance | Establish the “Code of Ethical Management” and other regulations to prevent unethical behavior. All business activities must comply with legal regulations to maintain the reputation and ensure sound operations. | Reducing the risk of corruption has a positive impact on economic activities. If the company is penalized, it will not only affect the interests of stakeholders but also result in financial losses and reputational damage. |
| Talent development and retention | Cultivate employees’ professionalism to improve working capabilities while offering compensation and benefits superior to peers so that employees can receive incentive and competitive remuneration. | Develop a comprehensive talent training blueprint and design a competitive compensation and benefits system to attract and retain outstanding talent, ensuring more stable corporate development. |
| Business performance and innovation strategy | FEDS enhances profitability through innovative, transformative and diversified business strategies, while striving to have a positive impact throughout its operations and continuously improving sustainable management practices and outcomes. | As the only department store in Taiwan featuring five generations of store transformation, FEDS has pioneered a new environmentally friendly shopping mall model, generating a positive economic impact while reducing negative environmental effects. |
