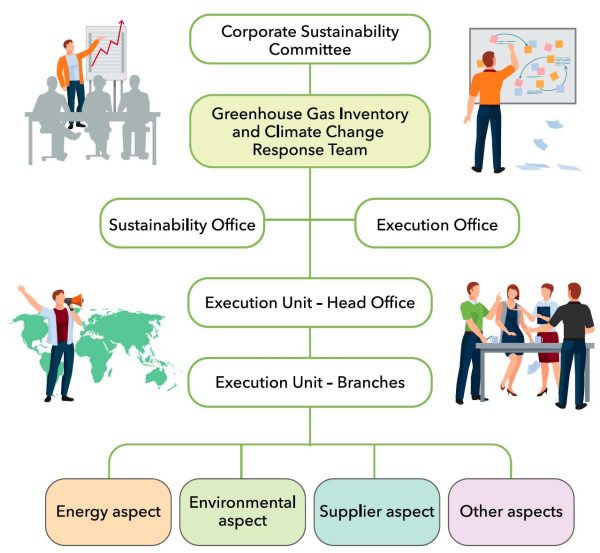
IPCC RCP climate scenario types and related indicators adopted by FEDS
- Estimated scenario: RCP 8.5
- Estimated period: Mid-century (2050)
- Climate-related data indicators:
- Variation in rainfall: The variation in the daily maximum rainfall in Taiwan is estimated to be about -4.8% to 41.7%, and the actual rainfall is about 209.6mm to 283.4mm.
- Variation in temperature: The annual average temperature in Taiwan increases by about 0.9°C to 2.2°C, and the annual average temperature is expected to reach 21°C to 22.3°C.
In terms of rainfall, based on the RCP 8.5 climate scenario assumptions, the maximum daily rainfall in Taiwan will increase up to 283.4mm. According to the definition of rainfall classification set by the Central Weather Bureau on March 1, 2020, The 24-hour cumulative rainfall of more than 200mm is considered torrential rain, which may cause local flooding or deluge. Taking the area where the head office of FEDS is located as an example, after analysis, it is found that there is no flooding in the location of the head office or the surrounding areas under the scenario of 200mm rainfall in 24 hours. However, under the scenario of 350mm rainfall in 24 hours, there may be about 0.5 to 1.0 meters of water accumulation in the surrounding areas, which may cause obstruction to the transportation of people and goods in terms of physical climate risk. It is necessary to pay close attention to climate-related information for early prevention.
In terms of annual average temperature in Taiwan, where FEDS’s head office and its branches may encounter the risk of temperature increase by 2°C under the RCP 8.5 scenario, and the temperature may reach 21°C to 22.3°C, which may result in the increase in air-conditioning electricity expense, the infrastructure costs and the preservation costs for some products.