Climate Governance
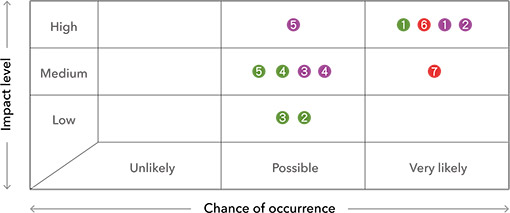
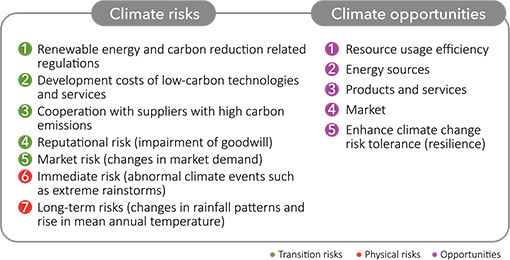
The climate governance framework of FEDS is overseen by the Board of Directors, which has established a “Greenhouse Gas Inventory and Climate Change Response Task Force.” After identifying climate-related impacts, meetings are held to discuss climate-related risks and opportunities, in order to adapt to and mitigate climate financial risks, while also identifying corresponding climate financial opportunities for implementation and policy promotion.
Since 2022, quarterly reports have been submitted to the Board of Directors on the progress of projects such as greenhouse gas inventory and verification. The Board reviews the content and direction of sustainability work and supervises the management team to make appropriate adjustments.